Methicillin is an antibiotic from the penicillin family, and MRSA is resistant to it (and often to other types of antibiotics). This makes infections harder to treat. MRSA was once considered mainly a hospital problem. Today, AK3 is entrenched in communities across New Zealand.
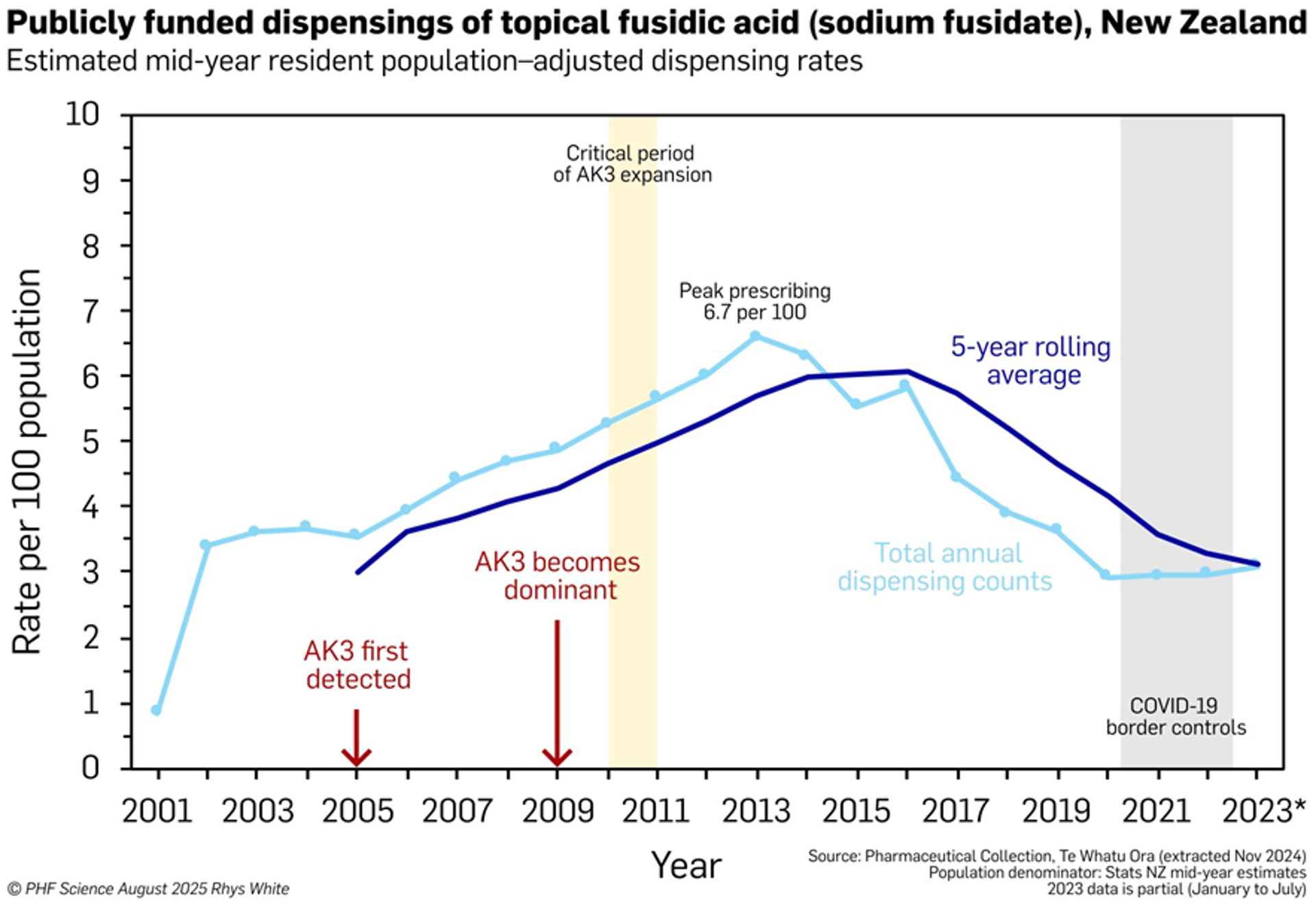
By sequencing and analysing hundreds of S. aureus genomes, our scientists traced AK3’s evolution from a drug-susceptible ancestor to a resistant superbug. New Zealand’s historic high use of the topical antibiotic fusidic acid has likely driven AK3’s development and spread.
Why this matters for New Zealand
- First detected in 2005: AK3 is now the most prevalent MRSA strain in New Zealand, with cases also reported in the South Pacific and Europe.
- Genomic surveillance revealed how it picked up key resistance genes, including those conferring resistance to methicillin and fusidic acid.
- Equity focus: Māori are three times more likely, and Pacific peoples nearly five times more likely, to experience serious S. aureus skin infections.
- One Health: The detection of AK3 from an unwell cow highlights the movement of resistance across human, animal, and environmental domains.
Protecting antibiotics as critical infrastructure
This study highlights the importance of antimicrobial stewardship (using antibiotics carefully and only when needed) and the role of genomic intelligence in safeguarding New Zealand’s health security.
PHF Science is a key partner in New Zealand’s coordinated One Health surveillance system. By combining national-level programmes in antimicrobial resistance surveillance, environmental health, genomics, and risk assessment with important partnerships across agencies, diagnostic laboratories, universities, and hospitals, PHF Science helps ensure that genomic intelligence is integrated into public health action.
Together, we must ensure antibiotics remain effective for New Zealanders.
References
White RT, Bakker S, Bloomfield M, Burton M, Elvy J, Eustace A, et al. 20 years later: unravelling the genomic success of New Zealand’s home-grown AK3 community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microbial Genomics 2025;11:001452 doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001452
Williamson DA, Zhang J, Ritchie SR, Roberts SA, Fraser JD, Baker MG. Staphylococcus aureus infections in New Zealand, 2000–2011. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2014;20:1156 doi: 10.3201/eid2007.131923

